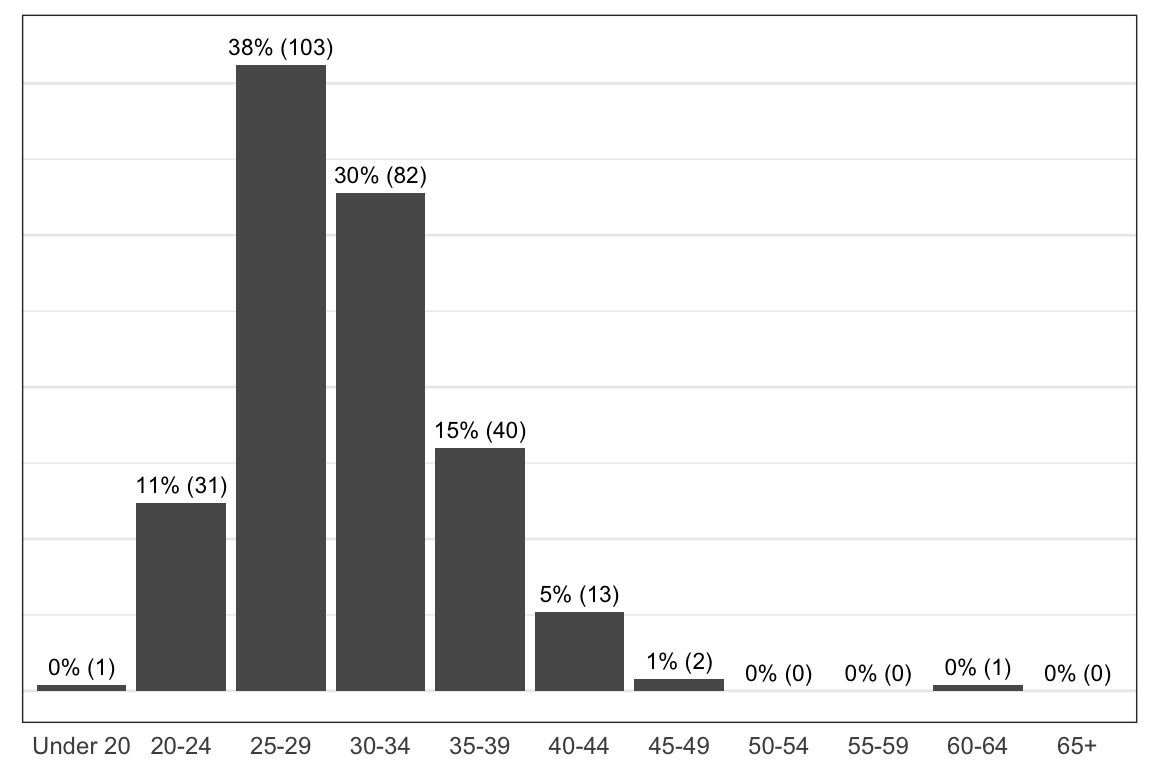
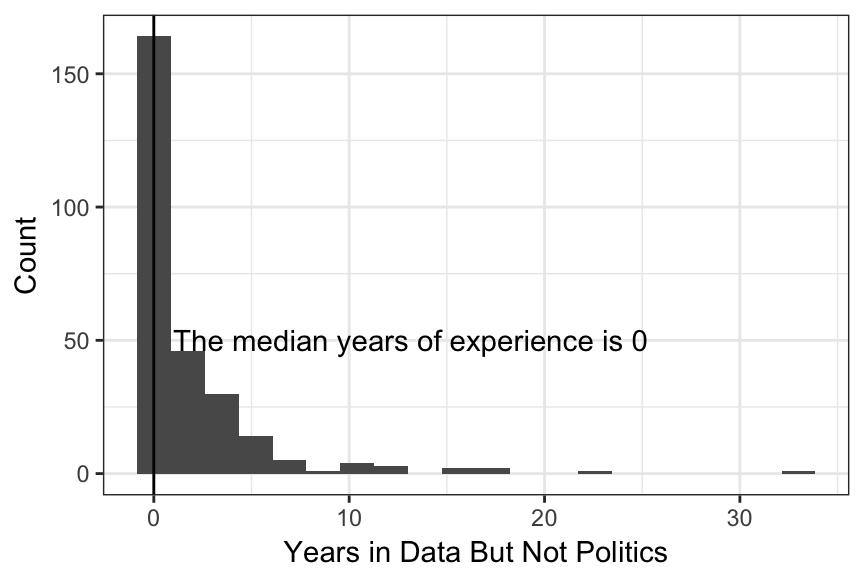
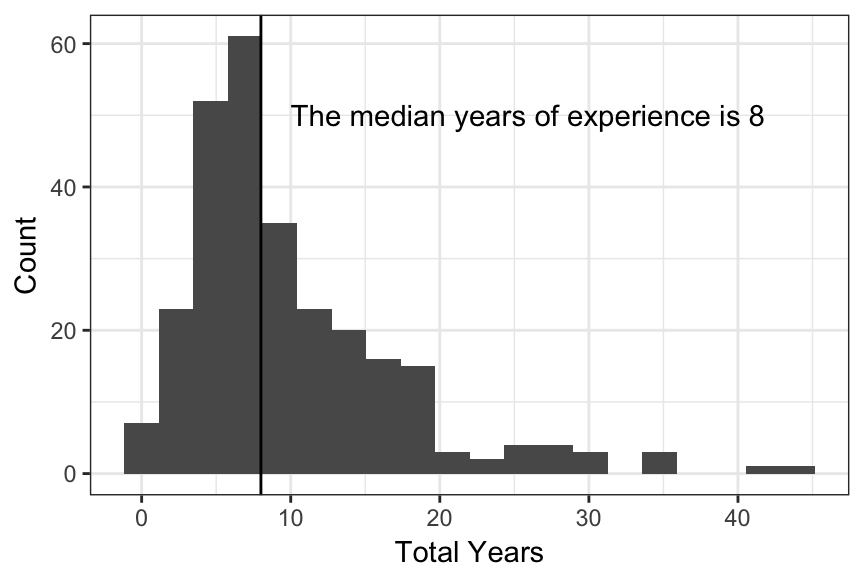
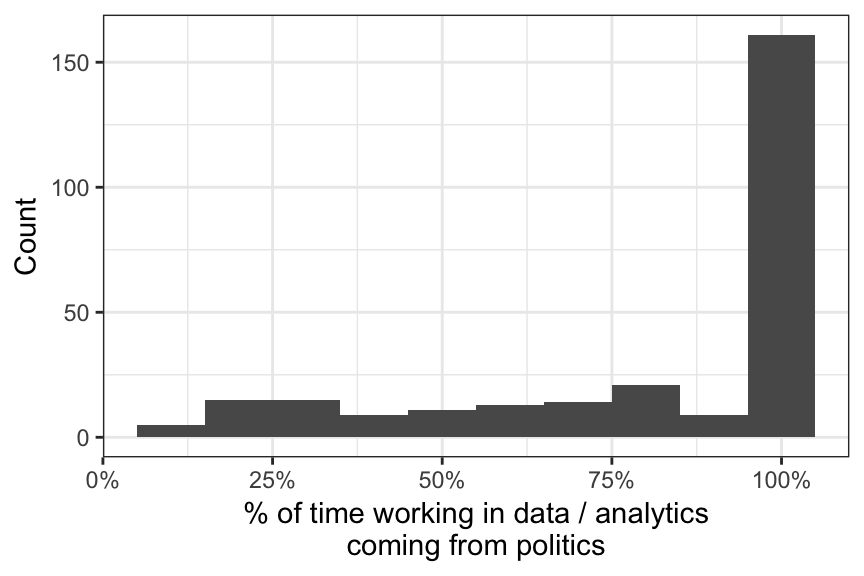
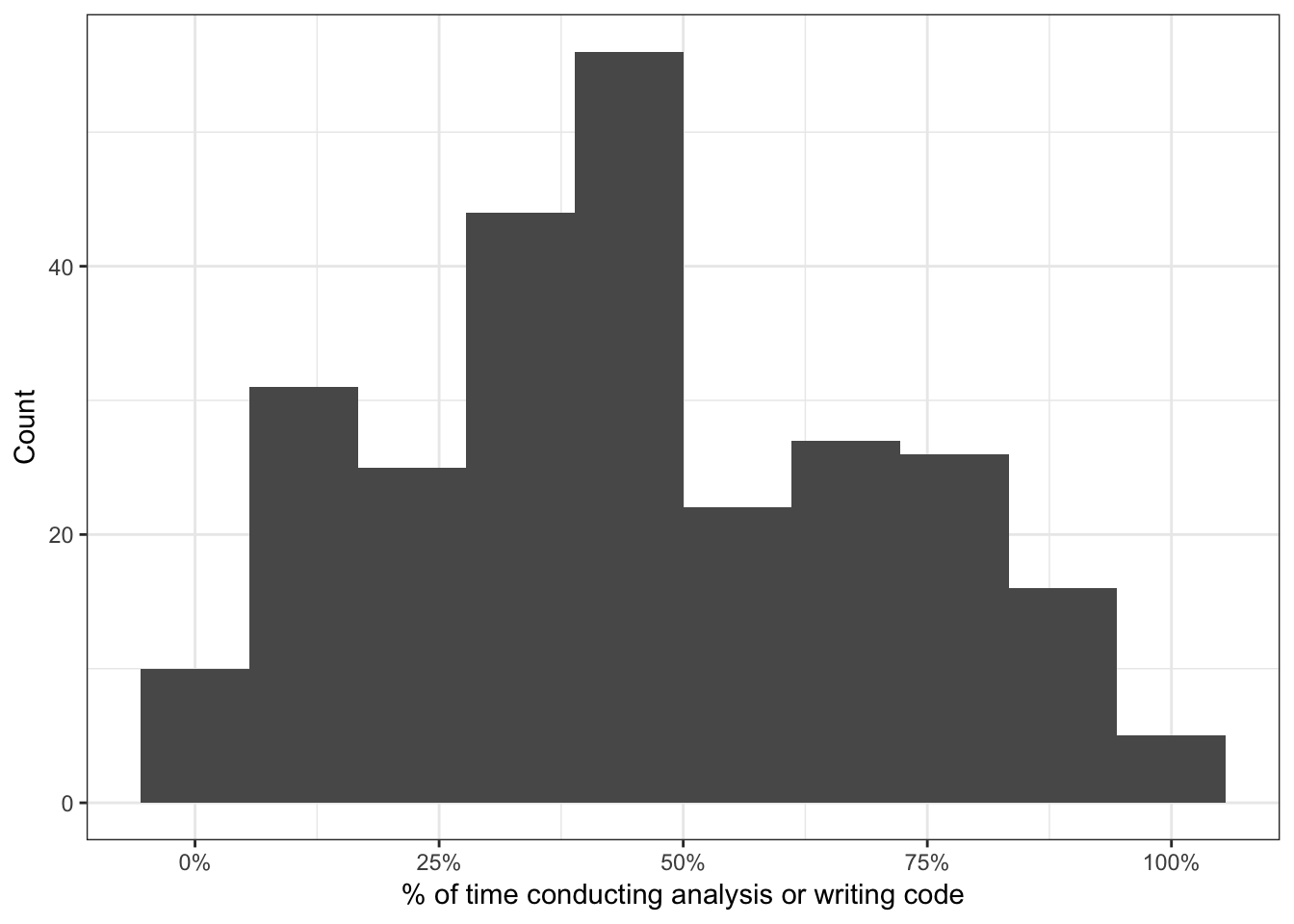
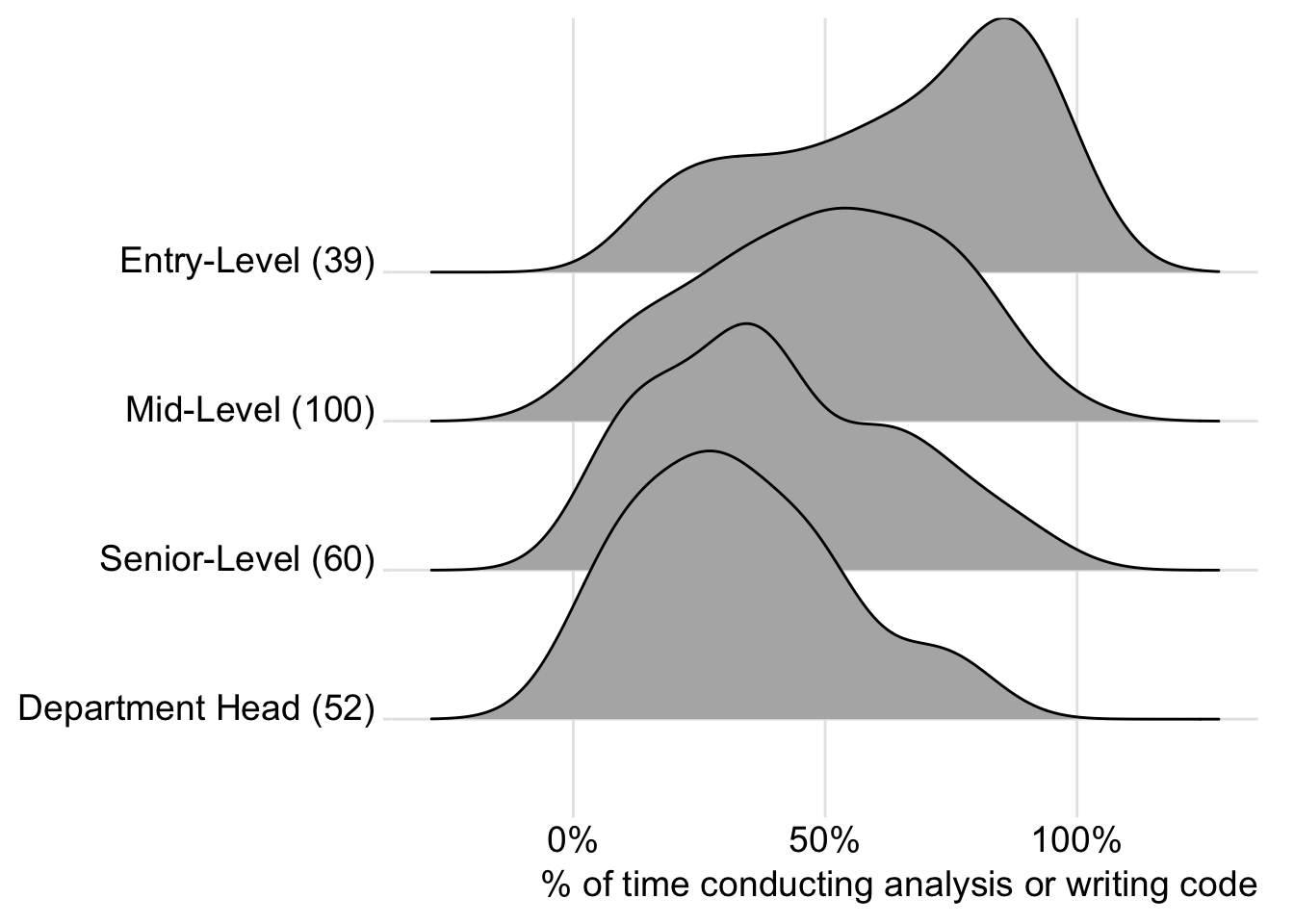
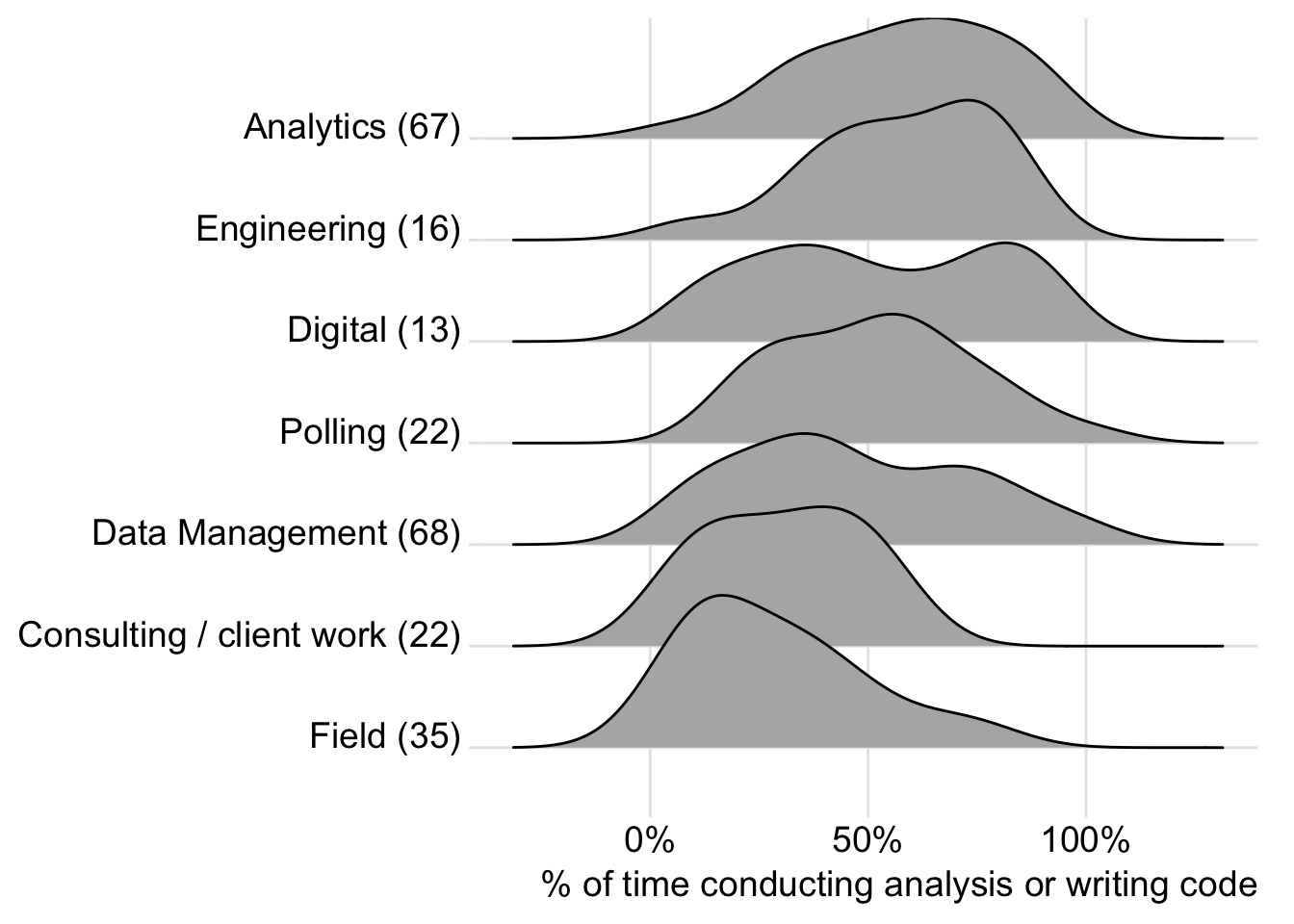
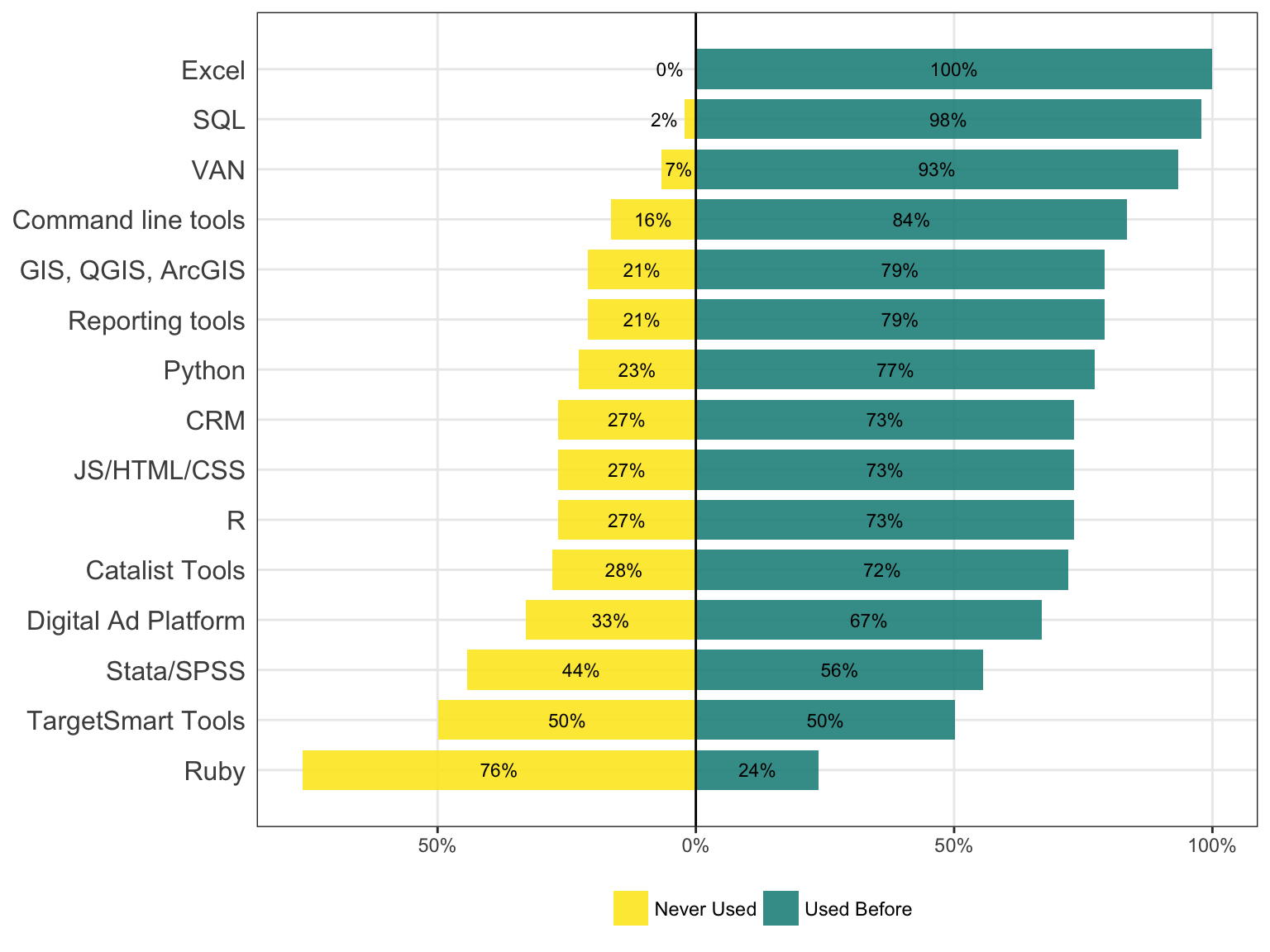
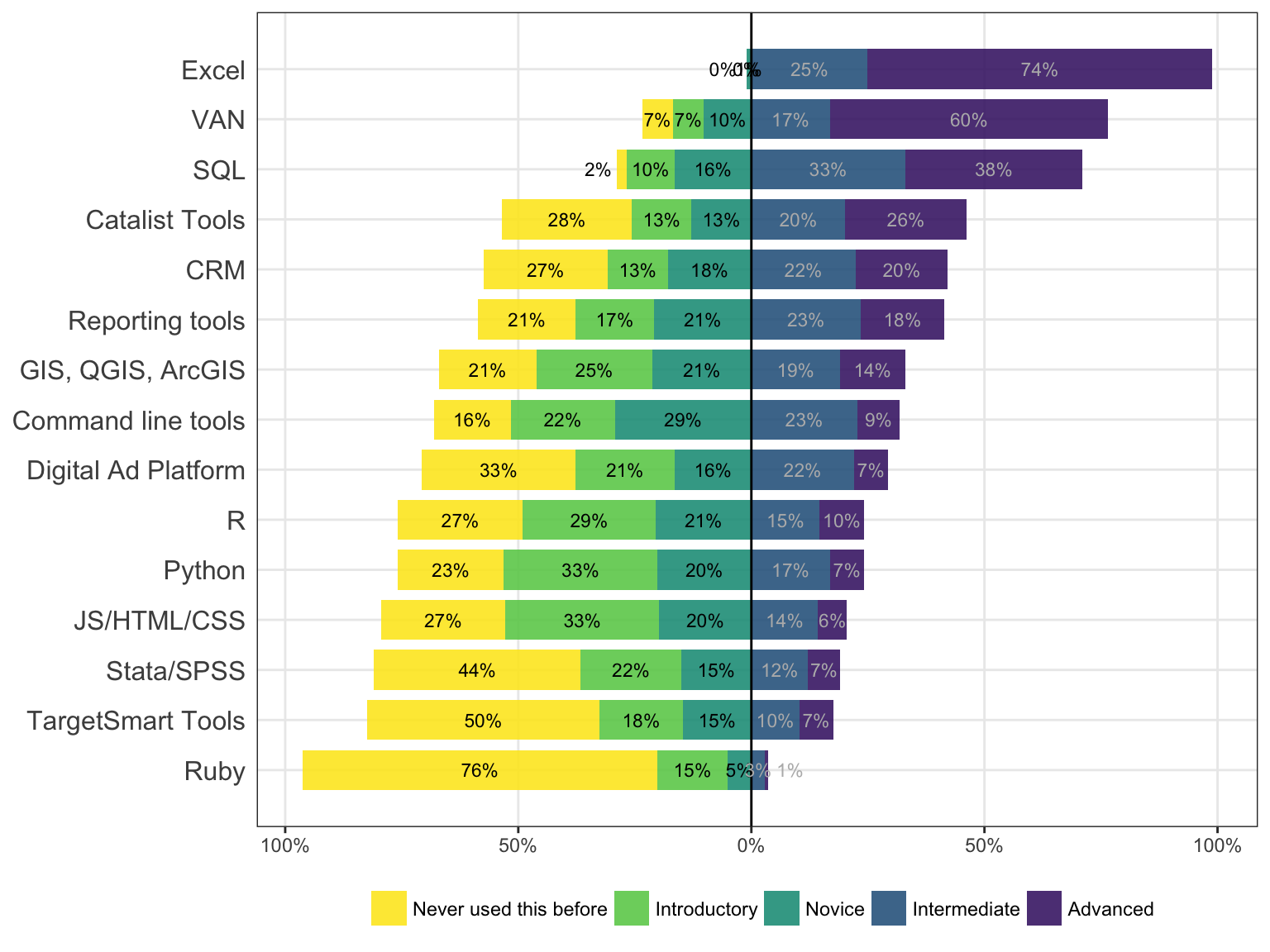
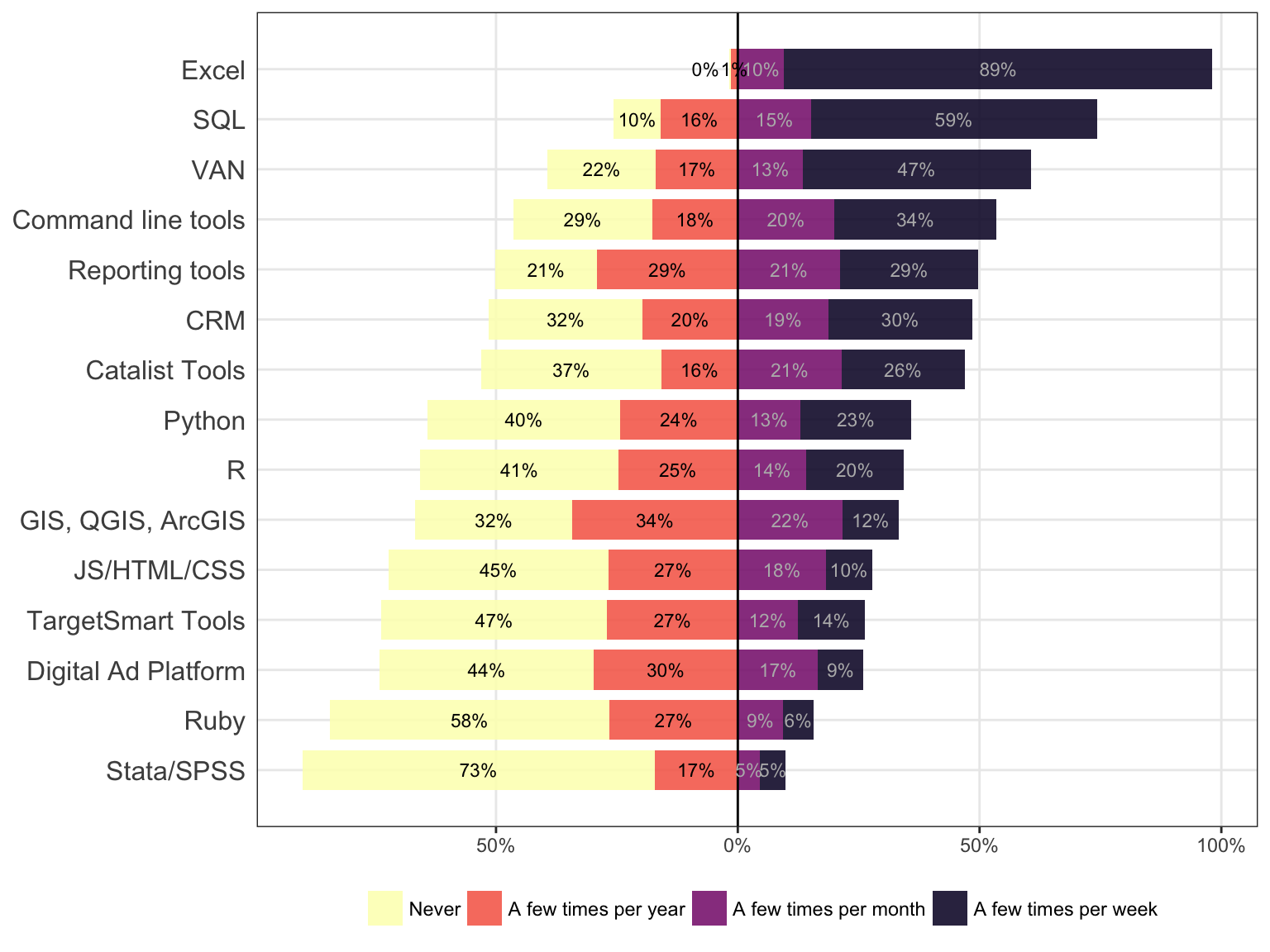
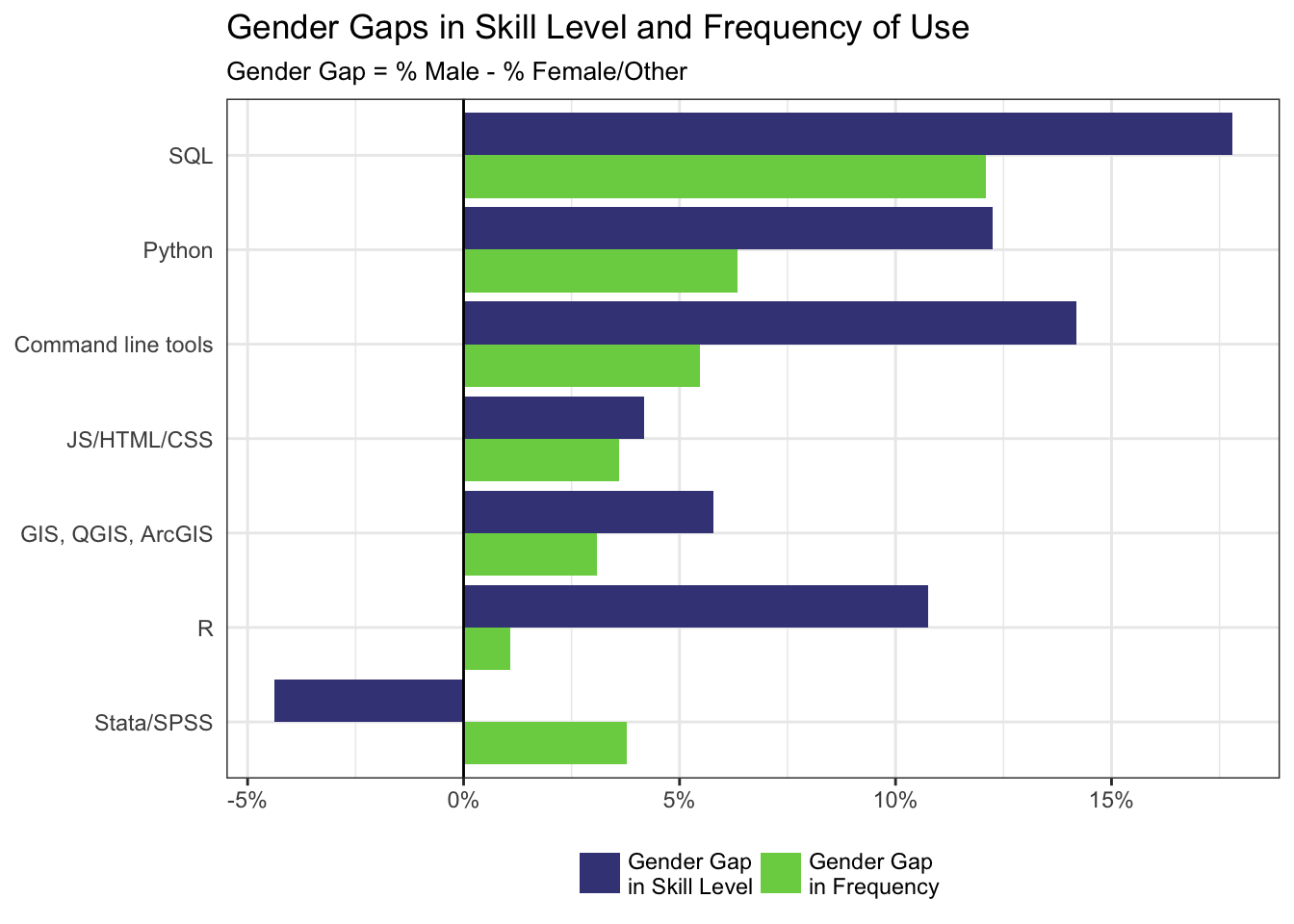
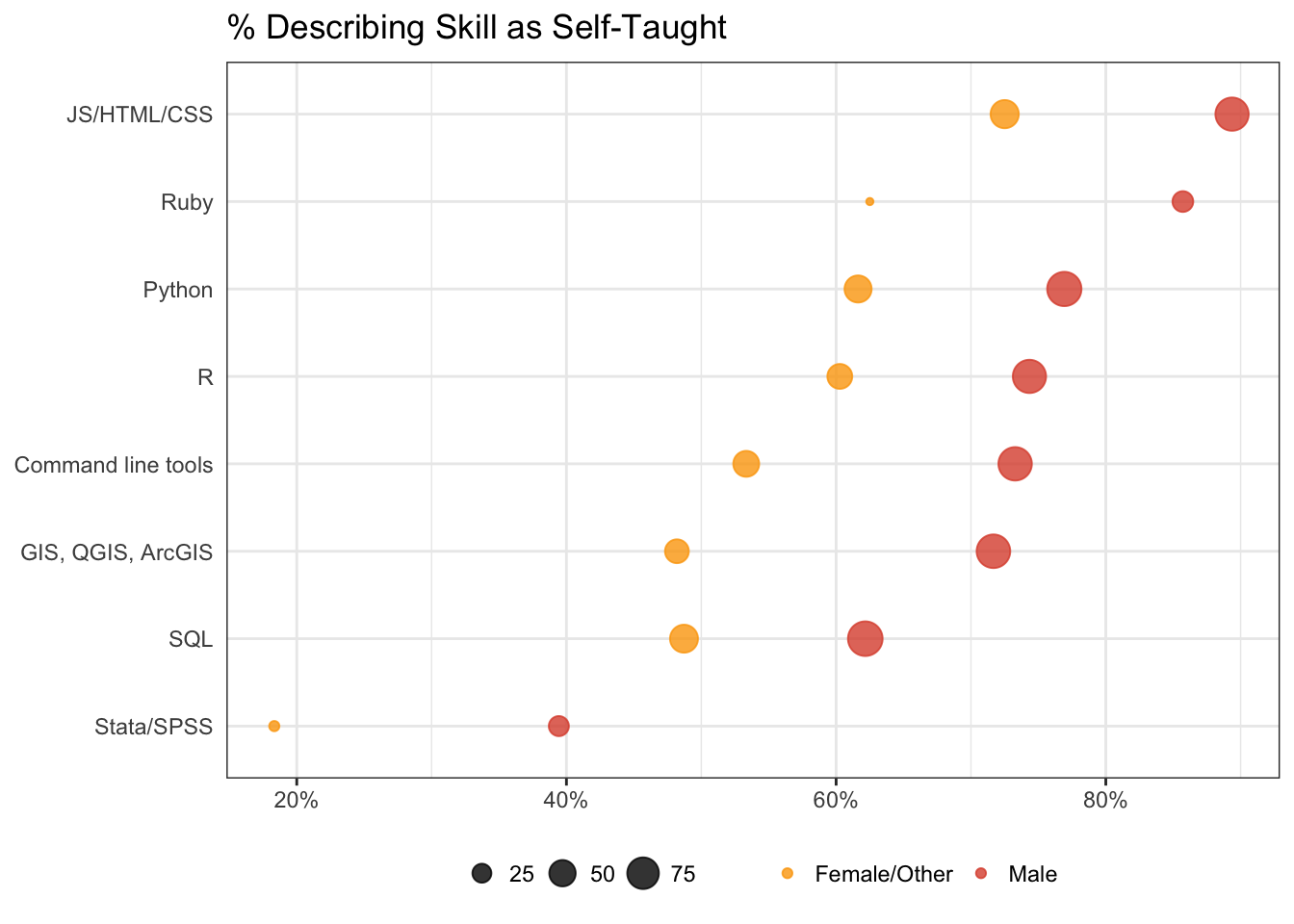
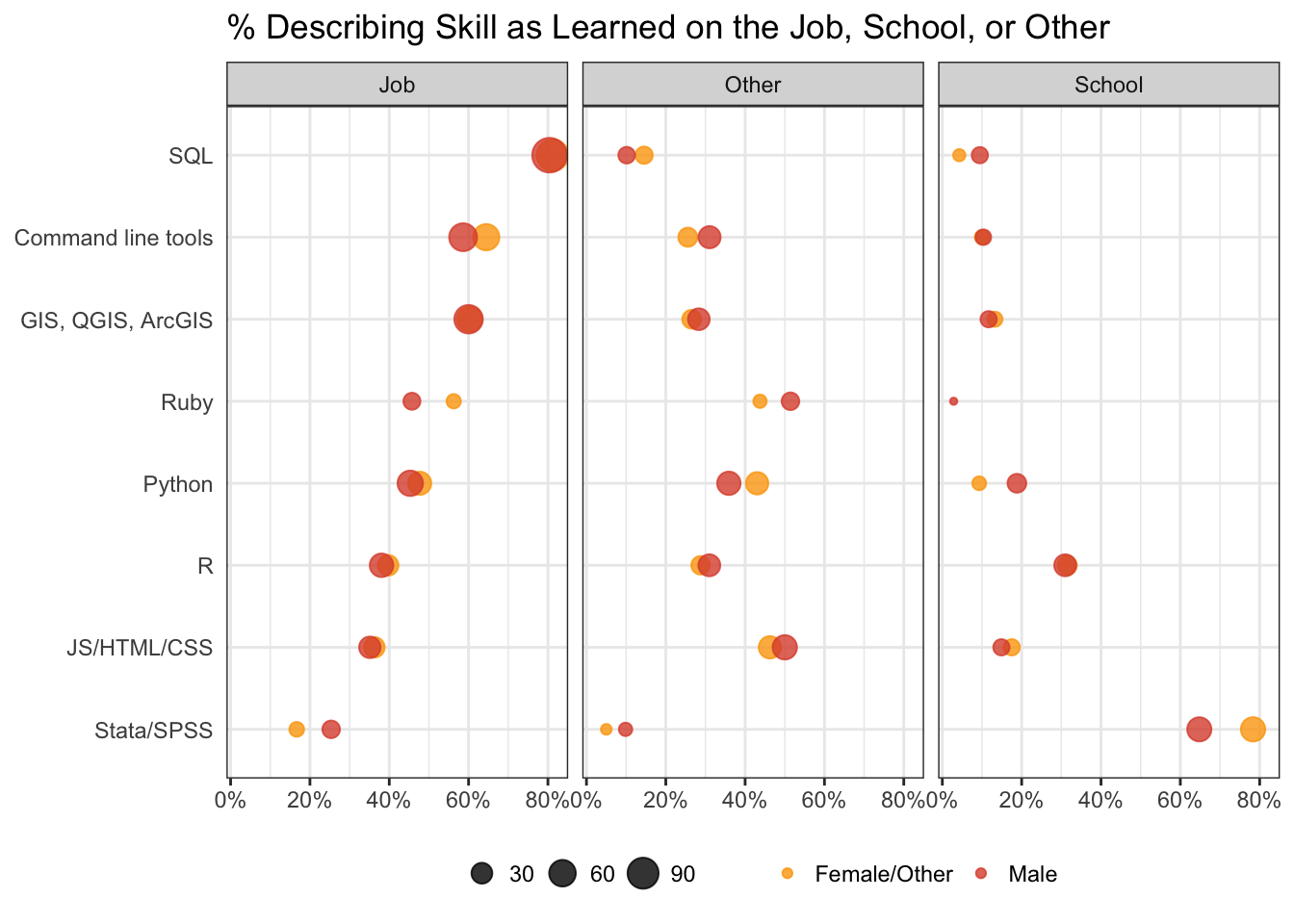
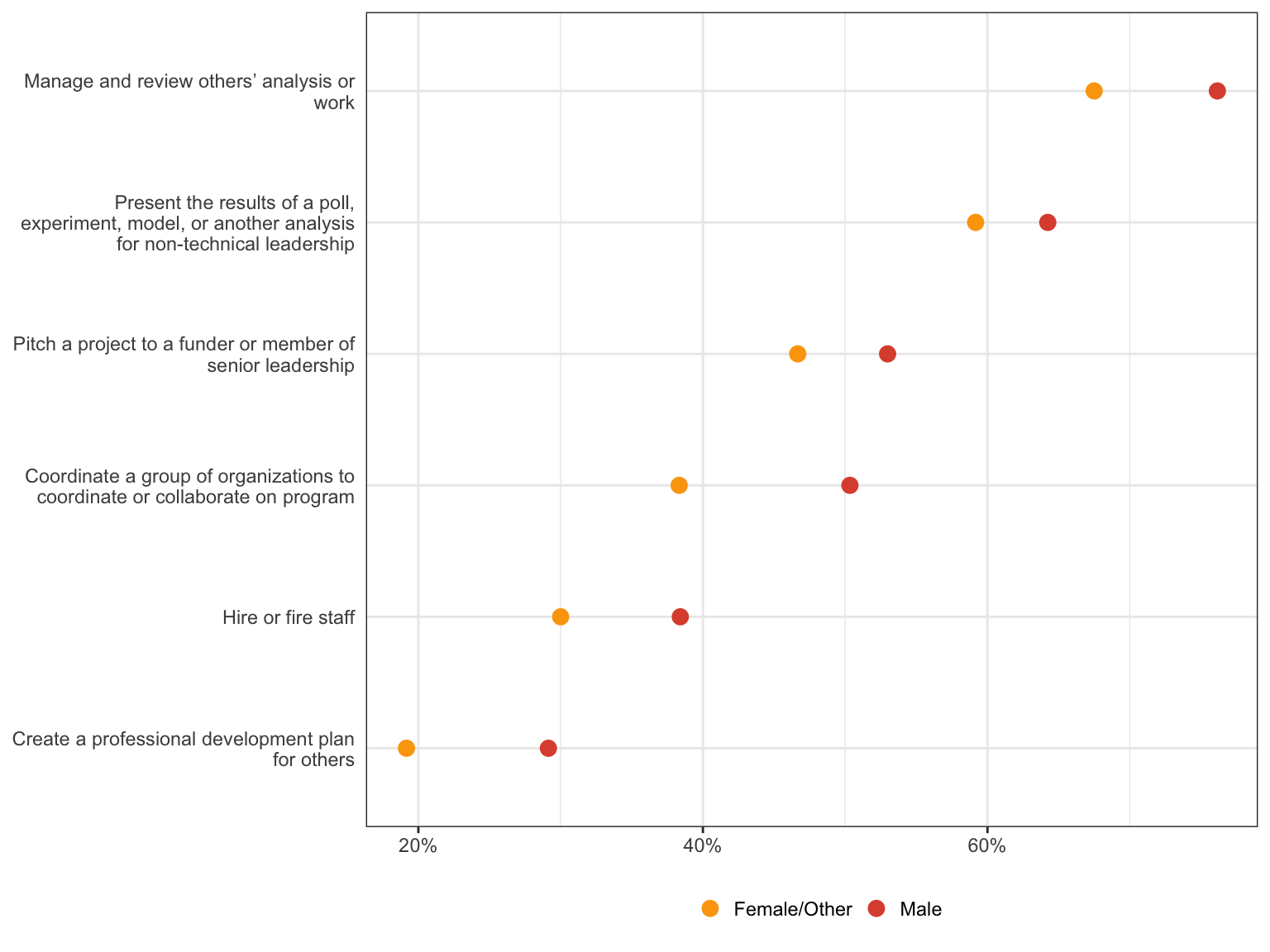
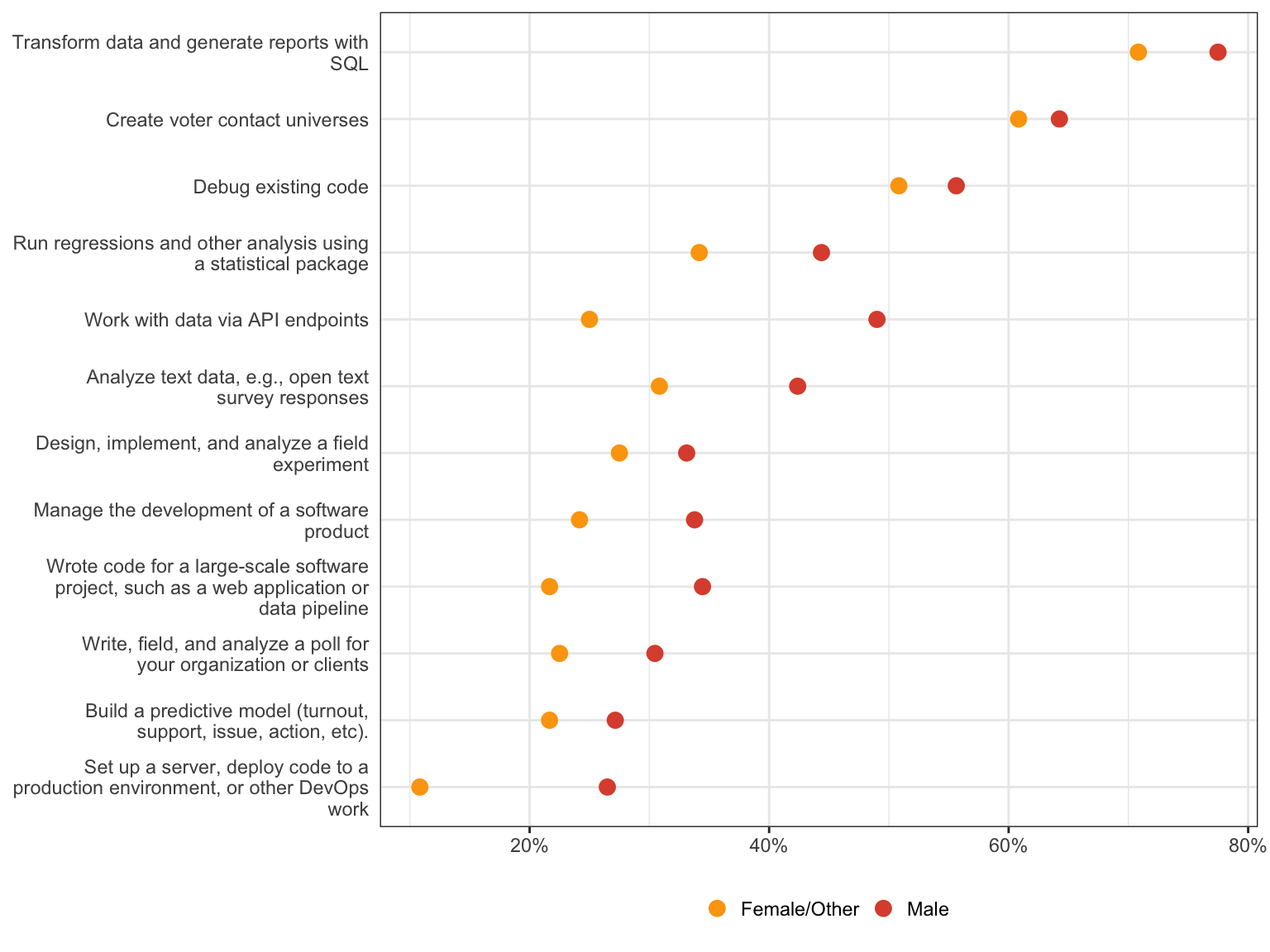
Which of the following most accurately describes the next step you would like to take to advance your career? Please select all that apply.
|
|
Proportion
|
|
Learn new skills or tools related to data, analytics, and technology
|
57%
|
|
Move into management or a more senior management role
|
45%
|
|
Work on more interesting/important projects as an individual contributor (i.e., not a manager)
|
29%
|
|
Stay in a similar role but move to another organization
|
26%
|
|
I’m happy where I am
|
26%
|
|
Leave politics
|
19%
|
|
Stay in politics but move out of data, analytics, and technology
|
12%
|
|
Start my own organization
|
10%
|
|
Other
|
5%
|
Write-in responses included wanting to work on a campaign, finishing school, rebuilding the union, growing an organization, leaving the US, and undecided.
For respondents who indicated that they wanted to leave politics, we asked an open-ended question about why they wanted to leave. Topics mentioned included
- Poor work-life balance (17)
- Lack of interest (15)
- Salary (8)
- Bad management (7)
- Lack of opportunities (5)
- Location (3)
Note that some responses mentioned multiple topics.
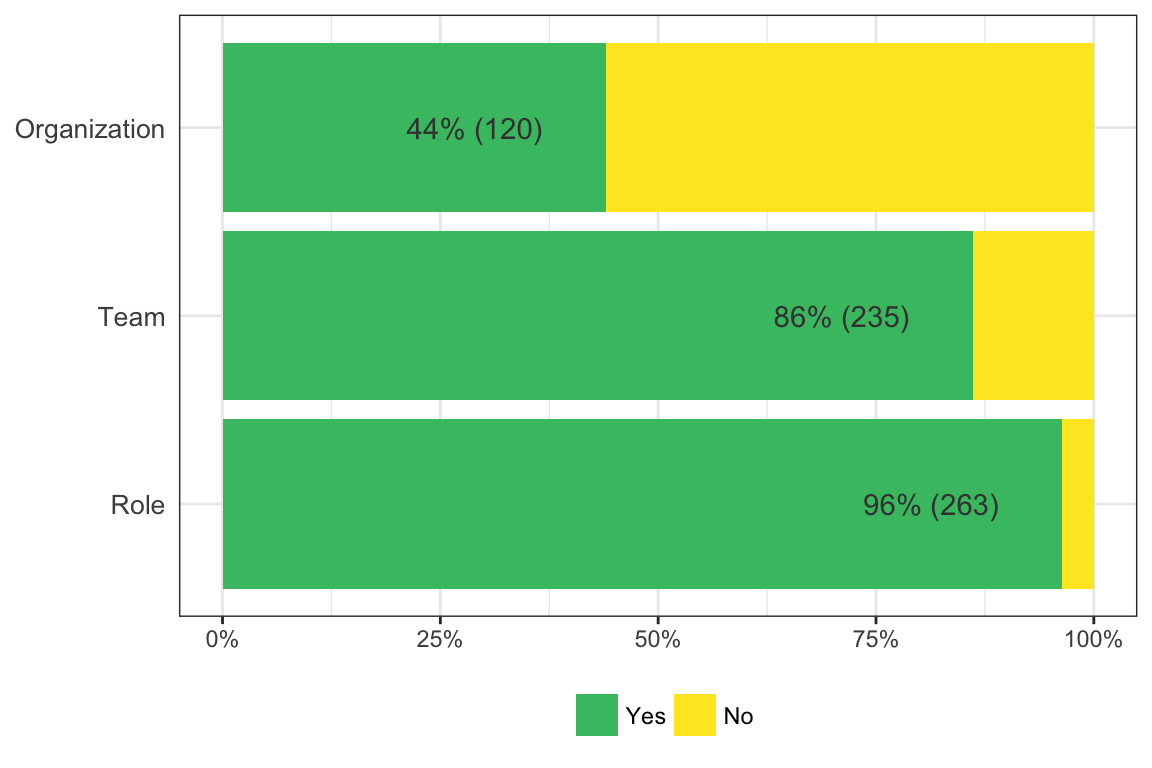
Are you planning to leave your organization within the next year? [only asked if respondent’s current employment status was not “Unemployed” or “Freelance”]
|
|
Proportion
|
N
|
|
I plan to actively look for new opportunities
|
17%
|
42
|
|
I might leave, but I’m not sure
|
35%
|
84
|
|
I’m not planning to leave
|
48%
|
115
|
Where do you want or expect to be working a year from now? Select all that apply. [only asked if respondents indicated (to the question about where they would be in one year) if they planned to actively look for new opportunities or if they might leave or if they indicated (to the question about next career steps) if they planned to move to another organization.]
|
|
Proportion
|
|
Analytics / Polling firm
|
50%
|
|
Issue or Advocacy Organization
|
46%
|
|
Political campaign
|
40%
|
|
Vendor (e.g., technology vendor)
|
32%
|
|
Other consulting firm (media, field, digital, etc.)
|
31%
|
|
Labor union
|
25%
|
|
Party committee
|
25%
|
|
Non-issue-specific Independent Expenditure group
|
17%
|
|
In School
|
12%
|
|
Other
|
22%
|
Thinking about the progressive data, analytics, and technology space, which one specific organization would you be most excited to work at? (Write-in)
161 respondents answered this question out of 273 total respondents. The proportions below display the percentage among those who responded. For a breakdown of these responses by gender and race, take a look at the Appendix.
|
|
Proportion
|
N
|
|
Civis Analytics
|
9%
|
15
|
|
Analyst Institute
|
9%
|
14
|
|
BlueLabs
|
8%
|
13
|
|
Democratic National Committee (DNC)
|
8%
|
13
|
|
Planned Parenthood Federation of America (PPFA)
|
5%
|
8
|
|
2020 Presidential
|
4%
|
6
|
|
Clarity Campaign Labs
|
3%
|
5
|
|
Google
|
3%
|
5
|
|
Catalist
|
2%
|
4
|
|
Democratic Congressional Campaign Committee (DCCC)
|
2%
|
4
|
|
NGP VAN
|
2%
|
4
|
The following organizations each had 3 votes: American Federation of Labor and Congress of Industrial Organizations (AFL-CIO), Freelance, National Democratic Redistricting Committee (NDRC), Obama Foundation
The following organizations each had 2 votes: American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU), American Federation of State, County and Municipal Employees (AFSMCE), Center for American Progress (CAP), City Government, Democratic Legislative Campaign Committee (DLCC), Gates Foundation, Global Strategies Group (GSG), Minerva Insights, National Education Association (NEA), Other, Pew Research, TargetSmart, Wellstone
The following organizations each had 1 vote: 18F, Action Network, Airbnb, America Votes, Association of Community Organizations for Reform Now (ACORN), Catalyst, Color of Change, Democracy Works, Democratic Senatorial Campaign Committee (DSCC), Emily’s List, Empower Engine, Every Town, Facebook, Federal Government, Gubernatorial Campaign, HaystaqDNA, Hustle, League of Conservation Voters (LCV), National Democratic Institute (NDI), National Security Agency (NSA), Precision Strategies, Progressive Change Campaign Committee (PCCC), Service Employees International Union (SEIU), ShareProgress, Sierra Club, Stacey Abrams for GA, State Party, The Victory Fund, Ultraviolet, United We Dream, US Census, US Institute of Peace